|
 Stem
Cells Stem
Cells  Red
Blood Cells Red
Blood Cells  White
Blood Cells White
Blood Cells
 Platelets Platelets
 Plasma Plasma
 Blood
Types & Activity Blood
Types & Activity
 Bloodology Bloodology

All of the blood cells in your body are produced in your
bones, inside the bone marrow.
Bone marrow looks like a network of tiny little connected caves,
similar to a honeycomb. Inside, are some very special parent cells
called stem cells. A stem cell can divide itself and produce a twin.
This process of cell division called mitosis. Through mitosis, the
stem cell can keep on creating more and more stem cells just like
itself.

|
 |

|
 |

|
 |
| Process of Cell Division or "Mitosis"
|
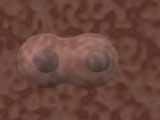
A stem cell can develop into all the other different blood cells
as well. The stem cell can actually differentiate into red cells,
white cells and platelets. Inside the cell, a structure called the
nucleus acts very much like a computer program.
 |
 |
It directs the cell to produce
a special protein called hemoglobin. And it's this hemoglobin
that makes red cells look red and gives them the ability to
attract and transport oxygen. |
| |
 |
 |
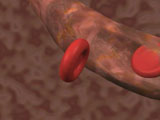
After the red
cell is full of hemoglobin, the job of the nucleus is done and
it gets kicked out. Then, the mature red cell has a little dip
in its middle on both sides. |
| |
 |
 |
At this point, the red blood
cell leaves the bone marrow and begins to circulate in the bloodstream. |
| |
 |
 |
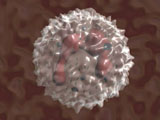
Through mitosis, stem cells
can also become many different kinds of white cells. |
| |
 |
 |
White cells are an extremely
important part of the body's immune system because they guard
the body against infections and diseases. |
| |
 |
 |
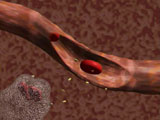
Stem cells can also become
many platelets. Platelets are extremely important in helping
blood clot when a cut is made. The stem cell turns into a factory
cell called a megakaryocyte. This is a very large cell with
several nuclei.
|
| |
 |
 |
The megakaryocyte never leaves
the bone marrow, but does produce many, many fragments. These
fragments are actually the platelets: small pieces of cell material
or cytoplasm. And they do leave the bone marrow and circulate
freely in the bloodstream.
|
| |
 |
 |
In addition to continuing
to produce all the cells in your own body, stem cells are also
extremely important in medicine and research.
|
| |
 |
 |
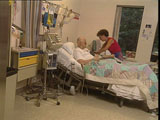
People who need a bone marrow
transplant because they are ill with a disease such as leukemia
or cancer, may receive new stem cells from the healthy bone
marrow of a volunteer donor through a transfusion.
When a bone marrow transplant does take place, it is only the
liquid part of the marrow that is donated, not the bone. It
is hoped that with this treatment, their own bodies will begin
producing a healthy variety of blood cells again.
|
|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Some terms
I got from the movie are platelets, plasma, bone marrow stem
cell mitosis, nucleus, oxygen and fibrin.
|
 |
—
Susanna,
elementary school student |
 |
 |
|
 |